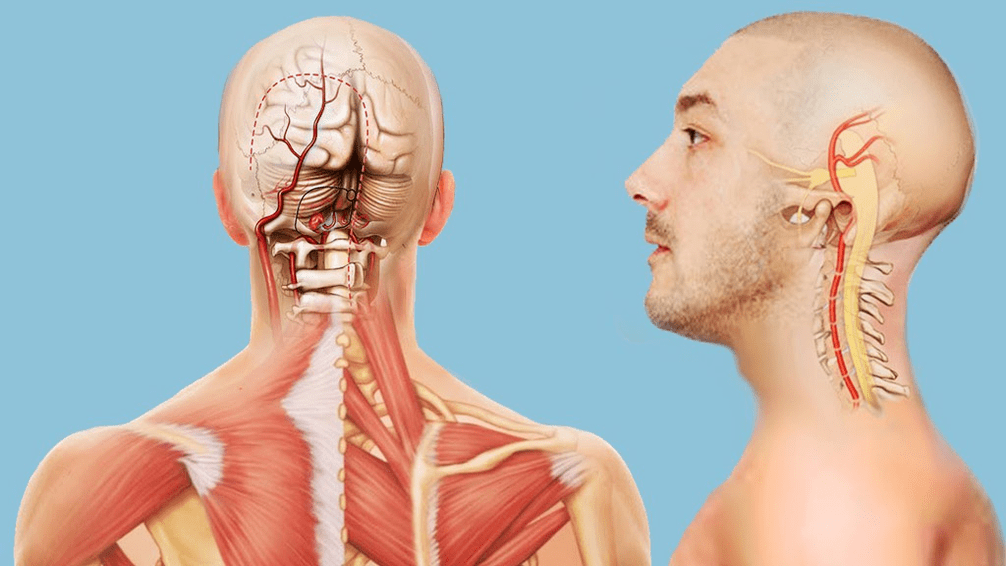
General signs and symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Pain in the back of the head, neck, and collar area
Noise, ringing, fullness in the ears
Dizziness
lack of air
nausea
vision problems
blood pressure soaring
Sudden fainting or syncope
Pharyngeal symptoms
Increased body temperature
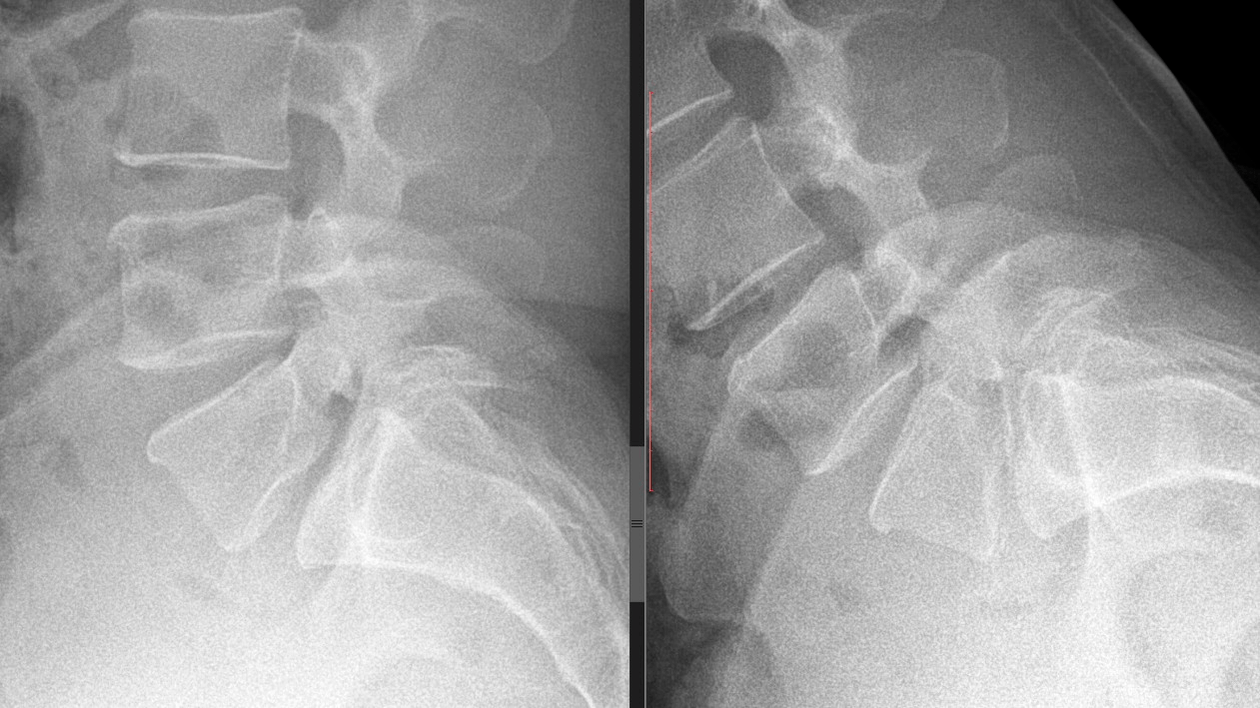
Symptoms depend on the stage of cervical osteochondrosis
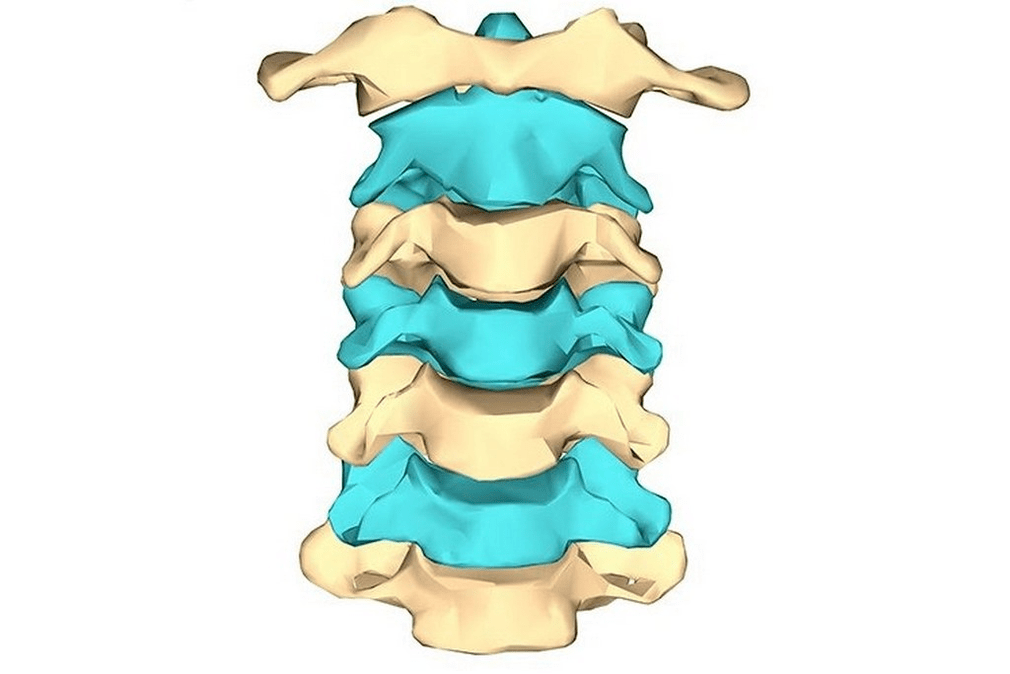
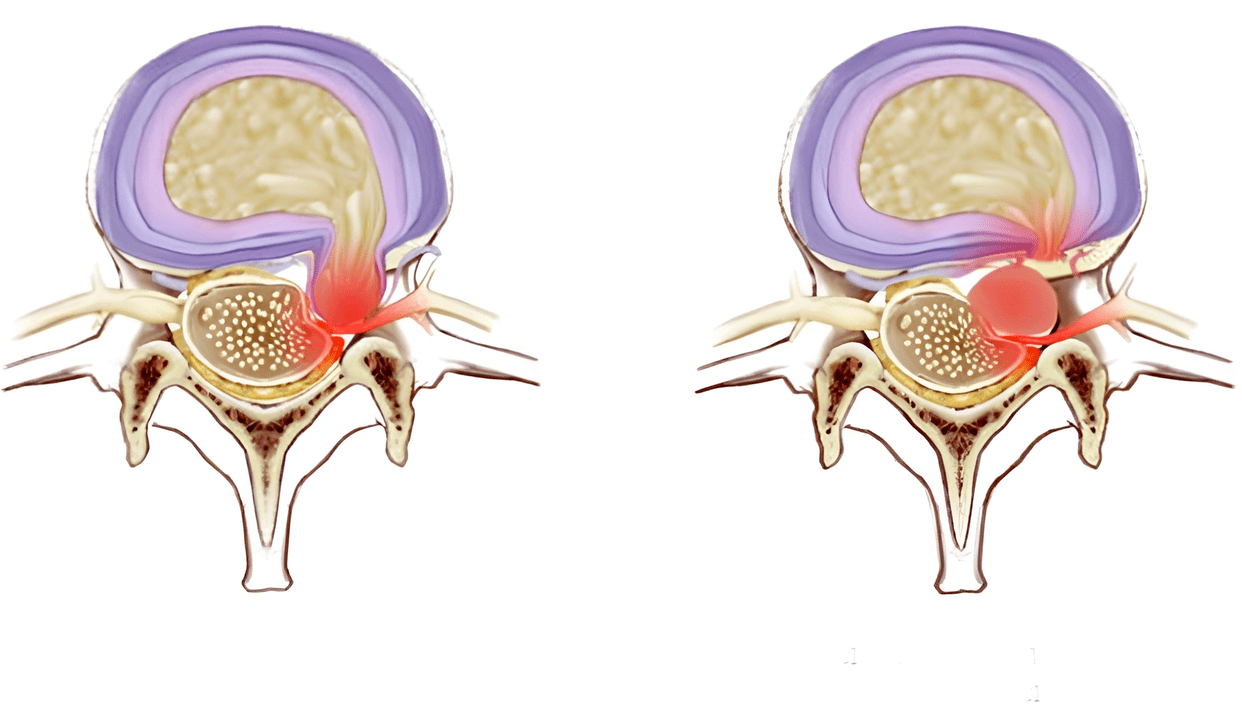
Syndromes caused by cervical osteochondrosis